Based on:

Disclaimer:
All the following information is based on the BlueInvest Investor Report, which combines market data with results from an investor survey conducted by BlueInvest. BlueInvest is a European Commission initiative launched in 2019 with the aim to accelerate new ocean-based technologies and solutions to unlock innovation and investment opportunities in the sustainable Blue Economy. It is funded by the European Maritime, Fisheries and Aquaculture Fund (EMFAF).
BLUE RENEWABLE ENERGY
Definition for the sector
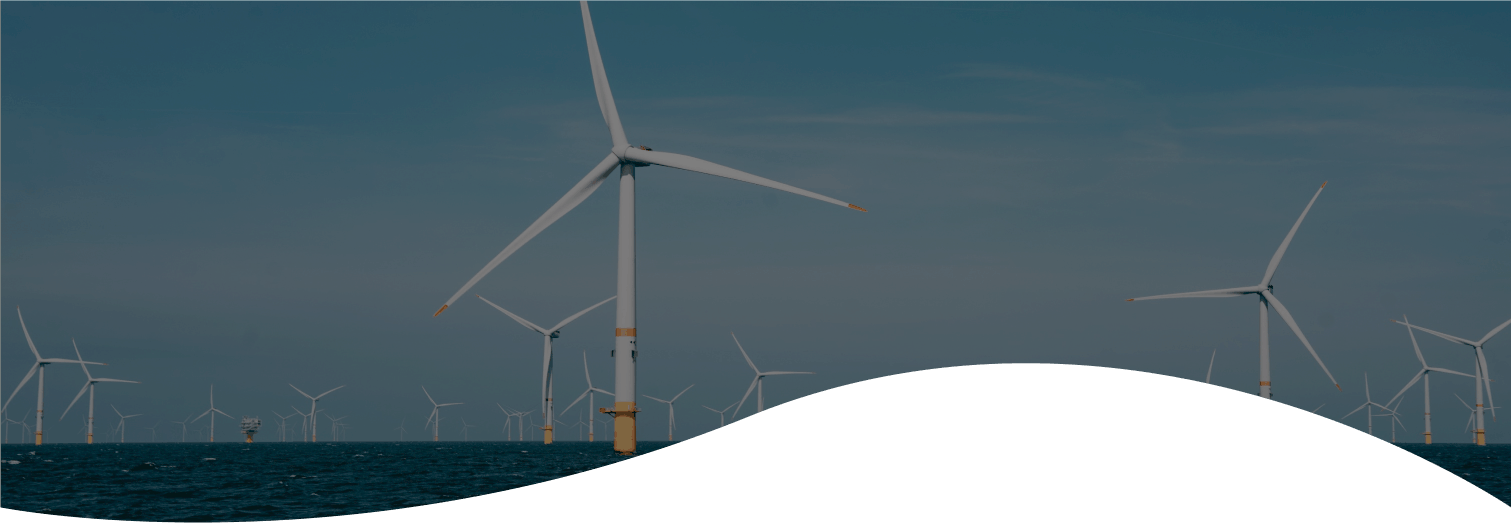
Blue renewable energy is the offshore, inshore and nearshore generation of clean and renewable power from natural sources or processes that are naturally replenished. It covers offshore wind energy, offshore photovoltaic production and ocean energy – technologies that exploit the potential of tides, waves, geothermal gradients and salinity gradients to generate clean power.
All these energy sources have the potential to connect to the grid (mass distribution national electricity grids), be used directly by end consumers (off-grid) or be transformed into blue fuel such as hydrogen, methanol or ammonia.
Worldwide, the technologies available for renewable marine energy production are at differing stages of maturity. Only offshore wind bottom-fixed technologies have been adopted and commercially deployed on a wide scale; most of the others are at early stages of development. Floating wind, tidal and wave energy devices have reached technological maturity and are in demonstration stage. As such, R&D activity is very important throughout the value chain of the blue renewable energy sector.
DDC Strategy - Digitalize, Decarbonize, Circularise
Blue renewable energy has huge potential to contribute to sustainability, as the production and distribution processes entail much less pollution than those of most energy sources. Unlike fossil fuels, which are not only dirty but finite too, renewable energy is quasi-infinite. Additionally, offshore renewables are not as limited by available space as onshore renewables are. Therefore, blue renewable energy offers a solution for serving the world’s needs in a sustainable and potentially scalable way.
Fórum Oceano Services for the sector
Business development and internationalization: market intelligence services; organization of business missions and matchmaking; support for investment initiatives; creation of ESG entrepreneurship and business acceleration programmes; support for business internationalization.
Business acceleration, entrepreneurship, digitalization and ESG innovation: implementation of European and extra-European projects focused on innovation ecosystems and networks; support services for the creation of ESG business models; ESG impact assessment services for companies and technologies; support for business financing; support for access to infrastructures for testing ESG technologies, products, and services.
Training, education, and literacy: Creation of technical and higher education training solutions; Development of blue literacy initiatives linked to ESG youth entrepreneurship and knowledge of ESG blue economy professions.
Organizing events and actions to communicate the ESG blue economy: Disseminating knowledge and good practices, fostering collaboration between stakeholders, and highlighting emerging opportunities in the ESG blue economy.
Strategic studies and public policy: Conducting strategic studies to define municipal, regional and national blue economy strategies.
Value Chain

Key Innovations and Technologies
| Innovation | Description | Value Proposition |
|---|---|---|
| Smart components | Bolts, joints and other components that are able to signal their self-deterioration and structural integrity to a centralised system for easy monitoring. | The use of smart components reduces the risk of problems in offshore structures, lowers the need for constant monitoring and allows for quick and localised interventions offshore. |
| Improved connection lines to the grid | The development of longer, more resilient and more dynamic cables that can handle higher voltages and lose less energy along the way. | The improved cables allow for larger wind farms, enable platforms to be built further from the coast and, in the case of dynamic cables, ensure floating wind plants can adapt to movement. |
| Grid-connectable floating wind farms | The installation of wind turbines on floating substructures that are tethered with mooring lines and anchors. The floating platforms do not require a structure to be fixed to the ocean bed and can therefore be built in deeper waters, further from the coast. | Floating wind farms expand the availability of energy production to many other places (particularly southern European countries), increase production (the winds further from the coast are stronger) and reduce coastal pollution, as well as noise and visual pollution for communities. |
| Improved viability of floating offshore photovoltaic | Photovoltaic arrays mounted on rafts that are anchored out in open water, with subsea cables to channel the power back to land. | This setup uses available space offshore and enables solar energy to be produced from the sun at open sea (away from barriers to sun exposure like buildings). |
| Floating tidal devices | Energy devices that can be placed where tidal energy is highest, producing energy from the rise and fall of tides. | These devices can significantly decrease the levelised cost of energy (LCOE) of tidal energy since tides are stronger and produce more energy on the surface, despite the higher risks associated with waves. |
| New designs and processes for wave energy systems | The development of new solutions for wave energy production that are less costly, more robust and durable, yet still light and flexible, so that they are better able to handle rough conditions at sea and produce high amounts of energy at the same time. | The systems enable higher amounts of energy to be produced from waves with significantly lower LCOEs, making the energy generation process profitable and, therefore, establishing wave energy as a viable alternative to other energy sources. |
| Osmotic energy systems | Power systems that harness the energy produced by the difference in the salt concentrations of river water and seawater. The systems may use one of two methods: reverse electrodialysis and pressure retarded osmosis. | Osmotic energy systems can be installed at river mouths and generate energy from the naturally occurring mixing of salt water and fresh water. They could potentially be embedded in desalination systems. |
| Offshore geothermal energy systems | Systems that harvest the energy contained in the heat emanating from the Earth’s core via marine environments. | Heat from the Earth is a constant source of renewable energy that could provide round-the-clock energy production regardless of climate conditions. |
| Hybrid electricity generating systems | Installations that integrate multiple energy sources within one offshore power system. Example combinations could be wave-solar or wave-wind. | Hybrid systems increase the predictability and reliability of energy supply, raise overall energy production, maximise space usage and optimise investment (e.g. by utilising common cables and infrastructure). |
| Multi-purpose technologies | Systems with multiple industrial purposes, one of which is energy production. They exploit synergies between the industries/purposes to increase efficiency (e.g. the use of a geothermal gradient energy system in sectors like desalination, aquaculture, water treatment, etc.). | Multi-purpose technologies enable economies of scope, optimise investment (e.g. by utilising common infrastructure) and increase the efficiency of Blue Economy sectors. |
| Digitisation of maintenance | The installation and use of (1) common digital interfaces between control systems, (2) connected sensors to measure the forces provided by plant structures, (3) digital twins to monitor changes of loads on structures in real time, and (4) cameras or drones to obtain information about the interventions and/or resources required. | All these technologies allow for fewer, shorter and less staff-intensive maintenance interventions, which reduces both the costs and the risks of operating energy-producing systems at sea. |
| Hydrogen from renewables | An electrolyser is installed on offshore wind turbines or other offshore systems to extract hydrogen from water. The hydrogen is then transported to shore through a dedicated pipeline. | Produced hydrogen from renewable sources can be stored in transportable batteries that can be used at a time convenient to the user, whereas on-grid energy must be used immediately or else it will be lost. Additionally, hydrogen batteries facilitate the production of energy further from the coast where connection to the grid might be inviable. |
Blue Renewable Energy Markets Data


Blue Economy Barometer


Hub Azul Dealroom


Euronext Lisbon


Blue Invest
Fórum Oceano is the managing entity of the Portuguese Sea Cluster, certified and recognised by the Ministry of Economy and the Sea, the Ministry of National Defence and the Ministry of Planning and Infrastructure.
With the support of

Headquarters
Delegation
© 2026 Fórum Oceano. All rights reserved. Developed by Yacooba Labs